目标函数
maxf(x1,x2)=21.5+x1sin(4πx1)+x2sin(20πx2)
−3.0≤x1≤12.1
4.1≤x3≤5.8
编码方式
本程序采用的是二进制编码精确到小数点后五位,经过计算可知对于 x1 其编码长度为18,对于 x2 其编码长度为15,因此每个基于的长度为33。
参数设置
种群大小 pop=100 ,交配池 Ppool=pop/2 ,变异概率 Pm=100 ,交叉概率 Pc=100 ,最大迭代次数 Gmax=300 ,自学习变异概率 Spm=0.05 。
算法步骤
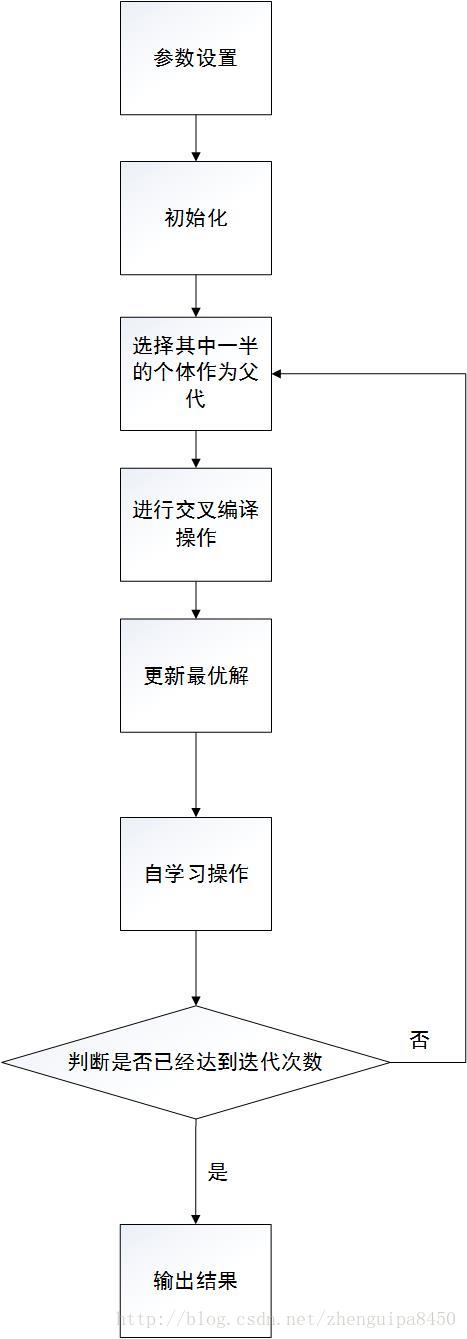
设计的程序主要分为以下步骤:1、参数设置;2、种群初始化;3、用轮盘赌方法选择其中一半较好的个体作为父代;4、交叉和变异;5、更新最优解;6、对最有个体进行自学习操作;7结果输出。其算法流程图为:
算法结果
由程序输出可知其最终优化结果为38.85029,
x1=11.625589,x2=5.725031
。
输出基因编码为[1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1]。
代码
import numpy as np
import random
import math
import copy
class Ind():
def __init__(self):
self.fitness = 0
self.x = np.zeros(33)
self.place = 0
self.x1 = 0
self.x2 = 0
def Cal_fit(x, upper, lower): #计算适应度值函数
Temp1 = 0
for i in range(18):
Temp1 += x[i] * math.pow(2, i)
Temp2 = 0
for i in range(18, 33, 1):
Temp2 += math.pow(2, i - 18) * x[i]
x1 = lower[0] + Temp1 * (upper[0] - lower[0])/(math.pow(2, 18) - 1)
x2 = lower[1] + Temp2 * (upper[1] - lower[1])/(math.pow(2, 15) - 1)
if x1 > upper[0]:
x1 = random.uniform(lower[0], upper[0])
if x2 > upper[1]:
x2 = random.uniform(lower[1], upper[1])
return 21.5 + x1 * math.sin(4 * math.pi * (x1)) + x2 * math.sin(20 * math.pi * x2)
def Init(G, upper, lower, Pop): #初始化函数
for i in range(Pop):
for j in range(33):
G[i].x[j] = random.randint(0, 1)
G[i].fitness = Cal_fit(G[i].x, upper, lower)
G[i].place = i
def Find_Best(G, Pop):
Temp = copy.deepcopy(G[0])
for i in range(1, Pop, 1):
if G[i].fitness > Temp.fitness:
Temp = copy.deepcopy(G[i])
return Temp
def Selection(G, Gparent, Pop, Ppool): #选择函数
fit_sum = np.zeros(Pop)
fit_sum[0] = G[0].fitness
for i in range(1, Pop, 1):
fit_sum[i] = G[i].fitness + fit_sum[i - 1]
fit_sum = fit_sum/fit_sum.max()
for i in range(Ppool):
rate = random.random()
Gparent[i] = copy.deepcopy(G[np.where(fit_sum > rate)[0][0]])
def Cross_and_Mutation(Gparent, Gchild, Pc, Pm, upper, lower, Pop, Ppool): #交叉和变异
for i in range(Ppool):
place = random.sample([_ for _ in range(Ppool)], 2)
parent1 = copy.deepcopy(Gparent[place[0]])
parent2 = copy.deepcopy(Gparent[place[1]])
parent3 = copy.deepcopy(parent2)
if random.random() < Pc:
num = random.sample([_ for _ in range(1, 32, 1)], 2)
num.sort()
if random.random() < 0.5:
for j in range(num[0], num[1], 1):
parent2.x[j] = parent1.x[j]
else:
for j in range(0, num[0], 1):
parent2.x[j] = parent1.x[j]
for j in range(num[1], 33, 1):
parent2.x[j] = parent1.x[j]
num = random.sample([_ for _ in range(1, 32, 1)], 2)
num.sort()
num.sort()
if random.random() < 0.5:
for j in range(num[0], num[1], 1):
parent1.x[j] = parent3.x[j]
else:
for j in range(0, num[0], 1):
parent1.x[j] = parent3.x[j]
for j in range(num[1], 33, 1):
parent1.x[j] = parent3.x[j]
for j in range(33):
if random.random() < Pm:
parent1.x[j] = (parent1.x[j] + 1) % 2
if random.random() < Pm:
parent2.x[j] = (parent2.x[j] + 1) % 2
parent1.fitness = Cal_fit(parent1.x, upper, lower)
parent2.fitness = Cal_fit(parent2.x, upper, lower)
Gchild[2 * i] = copy.deepcopy(parent1)
Gchild[2 * i + 1] = copy.deepcopy(parent2)
def Choose_next(G, Gchild, Gsum, Pop): #选择下一代函数
for i in range(Pop):
Gsum[i] = copy.deepcopy(G[i])
Gsum[2 * i + 1] = copy.deepcopy(Gchild[i])
Gsum = sorted(Gsum, key = lambda x: x.fitness, reverse = True)
for i in range(Pop):
G[i] = copy.deepcopy(Gsum[i])
G[i].place = i
def Decode(x): #解码函数
Temp1 = 0
for i in range(18):
Temp1 += x[i] * math.pow(2, i)
Temp2 = 0
for i in range(18, 33, 1):
Temp2 += math.pow(2, i - 18) * x[i]
x1 = lower[0] + Temp1 * (upper[0] - lower[0]) / (math.pow(2, 18) - 1)
x2 = lower[1] + Temp2 * (upper[1] - lower[1]) / (math.pow(2, 15) - 1)
if x1 > upper[0]:
x1 = random.uniform(lower[0], upper[0])
if x2 > upper[1]:
x2 = random.uniform(lower[1], upper[1])
return x1, x2
def Self_Learn(Best, upper, lower, sPm, sLearn): #自学习操作
num = 0
Temp = copy.deepcopy(Best)
while True:
num += 1
for j in range(33):
if random.random() < sPm:
Temp.x[j] = (Temp.x[j] + 1)%2
Temp.fitness = Cal_fit(Temp.x, upper, lower)
if Temp.fitness > Best.fitness:
Best = copy.deepcopy(Temp)
num = 0
if num > sLearn:
break
return Best
if __name__ == '__main__':
upper = [12.1, 5.8]
lower = [-3, 4.1]
Pop = 100
Ppool = 50
G_max = 300
Pc = 0.8
Pm = 0.1
sPm = 0.05
sLearn = 20
G = np.array([Ind() for _ in range(Pop)])
Gparent = np.array([Ind() for _ in range(Ppool)])
Gchild = np.array([Ind() for _ in range(Pop)])
Gsum = np.array([Ind() for _ in range(Pop * 2)])
Init(G, upper, lower, Pop) #初始化
Best = Find_Best(G, Pop)
for k in range(G_max):
Selection(G, Gparent, Pop, Ppool) #使用轮盘赌方法选择其中50%为父代
Cross_and_Mutation(Gparent, Gchild, Pc, Pm, upper, lower, Pop, Ppool) #交叉和变异生成子代
Choose_next(G, Gchild, Gsum, Pop) #选择出父代和子代中较优秀的个体
Cbest = Find_Best(G, Pop)
if Best.fitness < Cbest.fitness:
Best = copy.deepcopy(Cbest) #跟新最优解
else:
G[Cbest.place] = copy.deepcopy(Best)
Best = Self_Learn(Best, upper, lower, sPm, sLearn)
print(Best.fitness)
x1, x2 = Decode(Best.x)
print(Best.x)
print([x1, x2])





















 7868
7868











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








